In economic terms, "Zero Economic Profits" refers to a situation where a firm's total revenue exactly equals its total costs, including both explicit and implicit costs. This concept is also known as "zero economic profit" and is distinct from accounting profit.
Key Aspects of Zero Economic Profit
Definition and Calculation
Zero economic profit occurs when a firm's total revenue is equal to the sum of its explicit and implicit costs. The calculation takes into account not only the direct monetary costs (explicit costs) but also opportunity costs (implicit costs) associated with the use of resources.Distinction from Accounting Profit
It's important to note that zero economic profit does not necessarily mean the firm is making no money. A firm can have a positive accounting profit while simultaneously having zero economic profit. This is because accounting profit only considers explicit costs, while economic profit factors in both explicit and implicit costs.
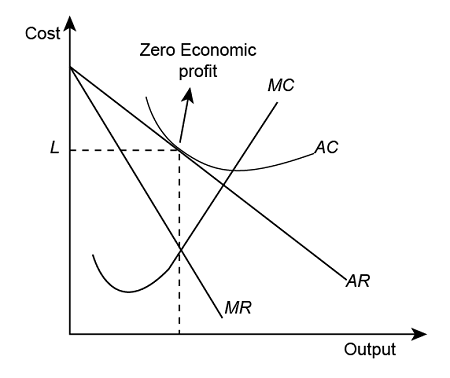
-
Long-Run Equilibrium
In perfectly competitive markets, zero economic profit is often associated with long-run equilibrium.In this situation:
Firms have no incentive to enter or exit the market
Resources are being used efficiently
Firms are earning just enough to keep them operating in the industry
-
Market Dynamics
The concept of zero economic profit plays a crucial role in understanding market dynamics:If economic profits are positive, it incentivizes new firms to enter the market
If economic profits are negative, firms are motivated to exit the market
When economic profits are zero, the market is in equilibrium, with no pressure for entry or exit
Implications and Significance
Resource Allocation
Zero economic profit indicates that resources are being allocated efficiently in the economy. Firms are earning just enough to keep their resources employed in their current use, rather than in the next best alternative.Competitive Markets
In highly competitive markets, the tendency towards zero economic profit in the long run helps explain why firms in such markets often operate on thin margins..Business Strategy
Understanding the concept of zero economic profit is crucial for businesses in assessing their performance relative to opportunity costs and in making decisions about market entry or exit.In conclusion, "Zero Profits" in economic terms represents a state of equilibrium where firms are covering all their costs, including opportunity costs, but not earning excess returns. This concept is fundamental to understanding market dynamics, resource allocation, and long-run equilibrium in competitive markets.
Zero-profit condition
Economic concept related to competitive markets
Definition - Occurs when the economic profit per firm in an industry is driven down to zero by competition
Market Competition - In a perfectly competitive market, firms continue to enter until there is zero profit per firm
Variables - Key variables include price of output (p), price of input (w), amount of output (f(x)), and amount of input (x)
Profit Function - Profit function is to maximize (price of output * amount of output) - (price of input * amount of input)
Contestable Markets Theory suggests that firms may set prices as if potential entrants were already in the market, even without actual entry
Zero profit is an important concept in economics, and its significance can be explained in simpler terms with some practical examples. Here's why it matters:
Market Equilibrium
Zero profit indicates a state of balance in the market. It's like a sweet spot where businesses are making just enough to keep going but not so much that everyone wants to jump in.
-
Example: Food Truck Business
Imagine a city where food trucks are becoming popular. At first, some trucks make big profits. This attracts more food truck owners to the area. As more trucks arrive, competition increases, and profits start to shrink. Eventually, the market reaches a point where food truck owners are making enough to cover all their costs (including the salary they could have earned elsewhere), but not much more. This is zero economic profit.
Resource Allocation
When industries reach zero profit, it suggests that resources are being used efficiently across the economy.
Example: Tech Startups
During a tech boom, many people might leave their jobs to start new companies. As the market becomes saturated, some startups succeed while others fail. Eventually, the industry settles into a state where starting a new tech company is about as profitable as other career options. This indicates that talent and resources are being distributed efficiently between tech and other sectors.
Long-term Sustainability
Zero economic profit doesn't mean businesses are failing; it means they're sustainable in the long run.
Example: Local Bookstore
A bookstore owner might earn enough to pay all the bills, pay herself a salary comparable to what she could earn elsewhere, and keep the store running smoothly. While she's not getting rich, the business is stable and can continue operating indefinitely. This is a state of zero profit.
Market Entry and Exit Decisions
The concept helps explain why businesses enter or leave markets.
Example: Rideshare Driving
When rideshare apps first launched, many drivers earned high profits. This attracted more drivers, increasing competition. Eventually, earnings settled to a point where driving was about as profitable as other similar jobs. At this point (zero economic profit), the number of drivers stabilizes – there's no rush of new drivers joining, nor are existing drivers quitting en masse.
Understanding True Profitability
Zero economic profit helps businesses and individuals make better decisions by considering all costs, including opportunity costs.
Example: Home-based Business
Someone might start a home-based business and celebrate making $50,000 in their first year. However, if they left a job paying $60,000, they're actually experiencing an economic loss of $10,000, even though they have a positive accounting profit. This understanding can help them make better decisions about continuing or changing their business strategy.
In summary, the concept of zero economic profit is important because it helps explain market behavior, guides resource allocation, indicates market stability, and assists in making informed business decisions. It's a key idea for understanding how markets function and how businesses operate in the long term.
Sources




Write A Comment